IaaS is a service of cloud computing: A service provider offers a virtualized IT infrastructure via the internet. The customer only rents the required components without purchasing them. They can then access this virtual infrastructure via broadband networks. The customer is only billed for the actual usage of the services.
Characteristics of IaaS
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) offers flexible resources, as companies can quickly scale their infrastructure as needed, especially during peak loads. Additionally, usage-based billing allows payment only for services actually used, eliminating high initial investments. Since the cloud provider always provides modern technology, users also benefit from secure and powerful infrastructure. Moreover, virtualization optimizes resource utilization and reduces costs by allowing companies to efficiently share their resources.
Advantages of IaaS
- Cost savings:
Companies avoid high investment costs and instead use flexible rental models. - Rapid implementation:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service enables quick deployment of new services. Users don’t have to wait for new hardware to be installed. - Scalability:
The model is particularly suitable for dynamically growing companies and start-ups. They can quickly adapt their resources to increasing demands.
IaaS Cloud Types
Public IaaS Cloud:
This infrastructure shares resources among many users. Access is via the internet.
Private IaaS Cloud:
Companies operate their own isolated cloud. It offers high security standards and control.
Hybrid IaaS Cloud:
Combines Public Cloud and Private Cloud to unite scalability and security. Sensitive data remains protected.
Responsibilities
Provider Responsibility:
The provider takes care of hardware, power supply, cooling, and security of the infrastructure.
Customer Responsibility:
The customer is responsible for operating systems, applications, data, and security aspects.
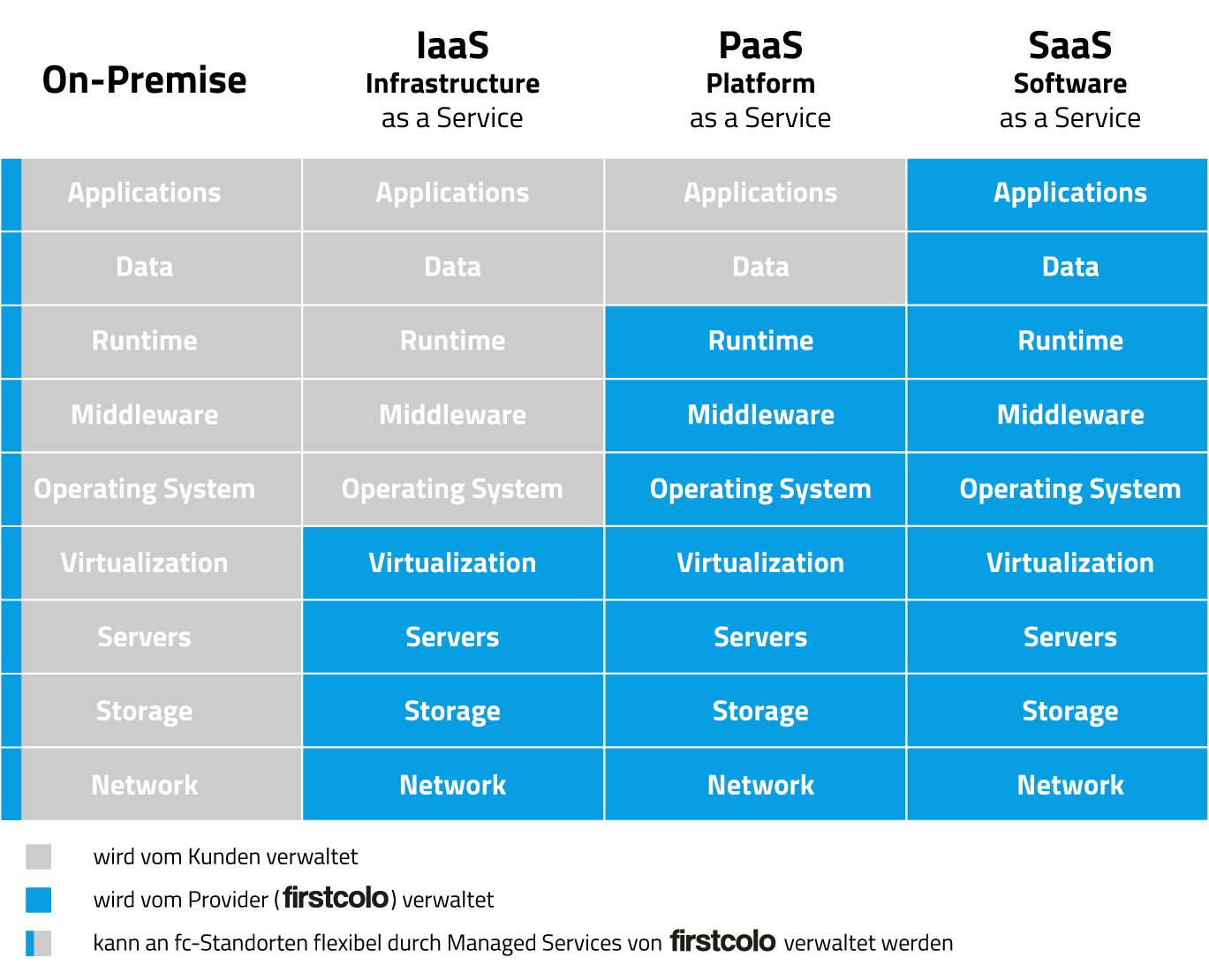
In the cloud service model Infrastructure-as-a-Service, responsibilities are distributed between the cloud provider and the customer as shown.
Application Possibilities
Infrastructure-as-a-Service is suitable for applications with variable computing capacity requirements. Development projects or online shops, for example, benefit from flexible resources. Companies can quickly respond to changing requirements without having to install additional hardware. For stable usage, considering own infrastructure might be an option.



